Personal injuries can occur unexpectedly and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, leading to pain, discomfort, and decreased mobility. Whether resulting from car accidents, workplace incidents, or everyday mishaps, these injuries require proper diagnosis and effective treatment to ensure a full recovery.
Understanding the most common types of personal injuries and their respective treatment options empowers individuals to seek appropriate care promptly. Lonseth Interventional Pain Centers is dedicated to providing comprehensive, personalized treatment plans that alleviate pain and promote healing, helping patients return to their daily activities with renewed comfort and confidence.
Whiplash
Whiplash is a neck injury caused by a rapid, forceful back-and-forth movement of the neck, similar to the cracking of a whip. This sudden motion can strain the neck muscles and ligaments, leading to pain and stiffness.
Whiplash most often occurs in car accidents, especially in rear-end collisions. It can also result from sports injuries, falls, or any situation where the neck is suddenly and forcefully jerked.
Common Treatments:
- Radiofrequency Nerve Ablation: This treatment involves using radio waves to heat and destroy specific nerve fibers, reducing pain signals from the affected area.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) Therapy: TENS therapy uses low-voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief by stimulating the nerves in the injured area and blocking pain signals to the brain.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises that improve range of motion and strengthen the neck muscles can aid in recovery and prevent long-term issues.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage symptoms during the initial recovery phase.
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc occurs when the soft center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This can irritate nearby nerves, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs.
Herniated discs are usually caused by gradual, age-related wear and tear on the spine (disc degeneration). It can also result from lifting heavy objects improperly, sudden injuries, or a traumatic event like a fall or a car accident.
Common Treatments:
- Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection: This procedure involves injecting steroids into the epidural space around the spinal nerves to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Lumbar Rhizotomy: Rhizotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that severs nerve roots in the spinal cord to relieve chronic back pain.
- Lumbar Sympathetic Blocks: These injections target the sympathetic nerves in the lower back to reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the spine, reducing the pressure on the herniated disc.
- Medication: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants are often prescribed to manage symptoms.
Wrist Fracture
A wrist fracture involves a break in one or more of the bones in the wrist. It’s a common injury, especially among people who fall and try to catch themselves with an outstretched hand.
The most frequent cause of a wrist fracture is a common fall onto an outstretched hand. Other causes include direct blows to the wrist, sports injuries, and car accidents.
Common Treatments:
- Casting or Splinting: Most wrist fractures can be treated with a cast or splint to immobilize the wrist and allow the bones to heal.
- Surgery: In cases where the bones are misaligned or the fracture is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign and stabilize the bones using plates, screws, or pins.
- Physical Therapy: Once the bone has healed, physical therapy helps restore strength and flexibility to the wrist.
- Pain Management: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can help manage discomfort during the healing process.
Spinal Fracture
A spinal fracture occurs when one or more bones in the spine (vertebrae) break. This type of injury can range from minor to severe, depending on the location and extent of the fracture.
Spinal fractures are often caused by traumatic events such as car accidents, falls from height, or sports injuries. Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones, can also make the spine more susceptible to fractures.
Common Treatments:
- Vertebroplasty: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting a special cement mixture into the fractured vertebra to stabilize the bone and relieve pain.
- Kyphoplasty: Similar to vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty involves inserting a balloon into the fractured vertebra to create space before injecting the cement, which can help restore some of the lost height of the vertebra.
- Bracing: A back brace may be used to immobilize the spine and allow the fracture to heal.
- Physical Therapy: Once the initial healing has occurred, physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
- Pain Management: Medications such as pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are often prescribed to manage pain during recovery.
Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain is a common condition characterized by discomfort in the lower region of the spine. It can be acute, lasting a few days to weeks, or chronic, persisting for three months or longer.
Lower back pain can be caused by muscle or ligament strain, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, arthritis, or simply poor posture. It can also result from injuries such as falls or car accidents.
Common Treatments:
- Lumbar Facet Joint Injections: These injections deliver a combination of steroids and anesthetic directly into the facet joints in the lower back to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Lumbar Radiofrequency Neurotomy: This procedure uses heat generated by radio waves to target specific nerves in the lower back, reducing their ability to send pain signals to the brain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles in the lower back, improving posture, and increasing flexibility can help alleviate pain.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and pain relievers can be used to manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, regular exercise, and ergonomic adjustments to workstations can help prevent recurrence of lower back pain.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. This pain typically affects only one side of the body.
Sciatica is most commonly caused by a herniated disc that presses on the sciatic nerve. Other causes include spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, and bone spurs on the spine. In some cases, muscle spasms or pregnancy can also contribute to sciatica.
Common Treatments:
- Lumbar Epidural Steroid Injection: This treatment includes injecting steroids directly into the epidural space around the spinal nerves to reduce inflammation and alleviate the pain associated with sciatica.
- Transforaminal Epidural Injections: This type of injection delivers steroids directly to the area where the nerve root exits the spine, providing targeted relief from pain.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises can help improve posture, strengthen the muscles around the spine, and reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help manage the symptoms of sciatica.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, proper lifting techniques, and ergonomic adjustments can help prevent the recurrence of sciatica.
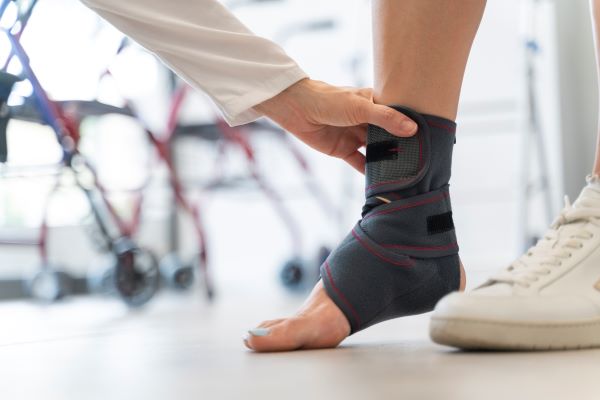
Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch or tear, typically due to a sudden twist or turn of the ankle. The severity of the sprain can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the ligament damage.
Ankle sprains are commonly caused by activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or uneven surfaces. They often occur during sports, but can also result from everyday activities such as walking or running on uneven ground.
Common Treatments:
- RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation): This standard treatment for sprains helps reduce swelling, relieve pain, and promote healing. Resting the ankle aims to prevent additional injury, while ice reduces inflammation. Compression involving an elastic bandage helps control the swelling, and elevating the ankle above the level of the heart can reduce fluid buildup.
- Physical Therapy: Once the initial swelling and pain subside, physical therapy can help restore strength, flexibility, and balance to the ankle.
- Bracing or Splinting: In certain cases, a splint or brace may be utilized to immobilize the ankle and allow it to heal properly.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Concussion
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that occurs when a blow to the head or a sudden jolt causes the brain to move rapidly back and forth within the skull. This movement can lead to chemical changes in the brain and sometimes stretch and damage brain cells.
Concussions are often caused by falls, sports injuries, car accidents, or any event that results in a direct impact to the head or a forceful shaking of the upper body.
Common Treatments:
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: This therapy involves structured mental exercises designed to improve cognitive functions that may be affected by a concussion, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Physical and mental rest is crucial during the initial recovery period. Gradual return to activities, guided by a healthcare professional, helps prevent further injury.
- Monitoring Symptoms: It’s important to monitor for worsening symptoms, such as persistent headaches, dizziness, or confusion, which may indicate a more serious injury.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers may be used to manage headaches and other symptoms, but should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Rotator Cuff Injury
Rotator cuff injuries involve damage to the grouping of tendons and muscles that surround the shoulder joint, helping to stabilize and move the shoulder. These injuries can vary from inflammation (tendinitis) to partial or complete tears of the tendons.
Rotator cuff injuries are commonly caused by repetitive overhead movements, such as those involved in certain sports (e.g., tennis, baseball) or occupations (e.g., painting, carpentry). They can also result from a sudden injury, like a fall, or gradual wear and tear associated with aging.
Common Treatments:
- Joint Injections for Shoulder Pain: These injections, often containing corticosteroids, help reduce inflammation and relieve pain in the shoulder joint.
- Soft Tissue Injection: This treatment involves injecting medication directly into the soft tissues around the shoulder to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to improve flexibility and strengthen the shoulder muscles can aid in recovery and prevent future injuries.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair a torn tendon or other damage within the rotator cuff.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the shoulder, along with proper rest, can help the healing process.
Knee Pain
Knee pain is a common complaint that can arise from various underlying conditions, including injuries, arthritis, and other degenerative issues. It can affect people of all ages and may involve the bones, cartilage, ligaments, or tendons surrounding the knee joint.
Knee pain can result from acute injuries such as ligament tears, meniscus injuries, or fractures. Chronic conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or tendinitis are also common causes. Overuse, poor biomechanics, or a previous injury can contribute to ongoing knee pain.
Common Treatments:
- Soft Tissue Injection: This treatment involves injecting medication, such as corticosteroids, into the soft tissues around the knee joint to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and addressing any biomechanical issues can help reduce pain and improve function.
- Bracing or Support: Wearing a knee brace or support can help stabilize the joint and relieve pressure on the affected area.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain relievers are commonly used to manage knee pain and reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, low-impact exercise, and avoiding activities that exacerbate knee pain can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage.

When You Should See a Doctor for Personal Injuries
While some personal injuries may seem minor at first, they can lead to more serious complications if not properly treated. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, swelling, numbness, or difficulty moving the affected area. Additionally, if your symptoms persist or worsen over time, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
At Lonseth Interventional Pain Centers, we specialize in providing comprehensive care for a wide range of personal injuries. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you manage pain and restore your quality of life. Don’t wait for your symptoms to escalate—schedule an appointment with us today to start your journey toward recovery.
